On Saturday 30th January I attended the first online Moth Recorders’ Meeting of 2021, organised by Butterfly Conservation and chaired by Dr. Richard Fox. Although it was still a couple of months from the time when people would be putting their traps out in earnest for the spring/summer influx of species on the wing, there was a poignant and reflective look back on the strange year that had just been. It was also noted how, through national lockdowns and social distancing measures brought on by the global pandemic in 2020, there had been an indisputable increase in appreciation for the importance of moths and butterflies. It was mentioned that, at the time of the meeting, there had been 14 million impressions across social media platforms using the hashtag #mothsmatter and an insatiable appetite for the Butterfly Conservation hawk-moth identification sheets and for moth traps!

The first talk of the morning from Dr. Zoe Randle discussed the connection to wildlife that was kindling in our homes and gardens through 2020, and reported that there was, in the last year, a 62% increase in records submitted to Devon Moth Group, and a 72% increase in recorders! This speaks volumes about a growing awareness and appreciation for moths and provides vital data on the bigger picture of how our native species are faring. There is also evidence to suggest that 2020 was a boom year for the Jersey Tiger moth, with abundant national sightings indicating that the species could be expanding its range further north.
Inevitably, this influx of records requires consolidation by county moth recorders on local levels in order to feed them into the national dataset, and it was these hard working volunteers who were the focus of Zoe’s talk. Specifically she discussed the best ways to support them in their rolls and investigated the demographics of county moth recorders alongside details on the submission status at the time.
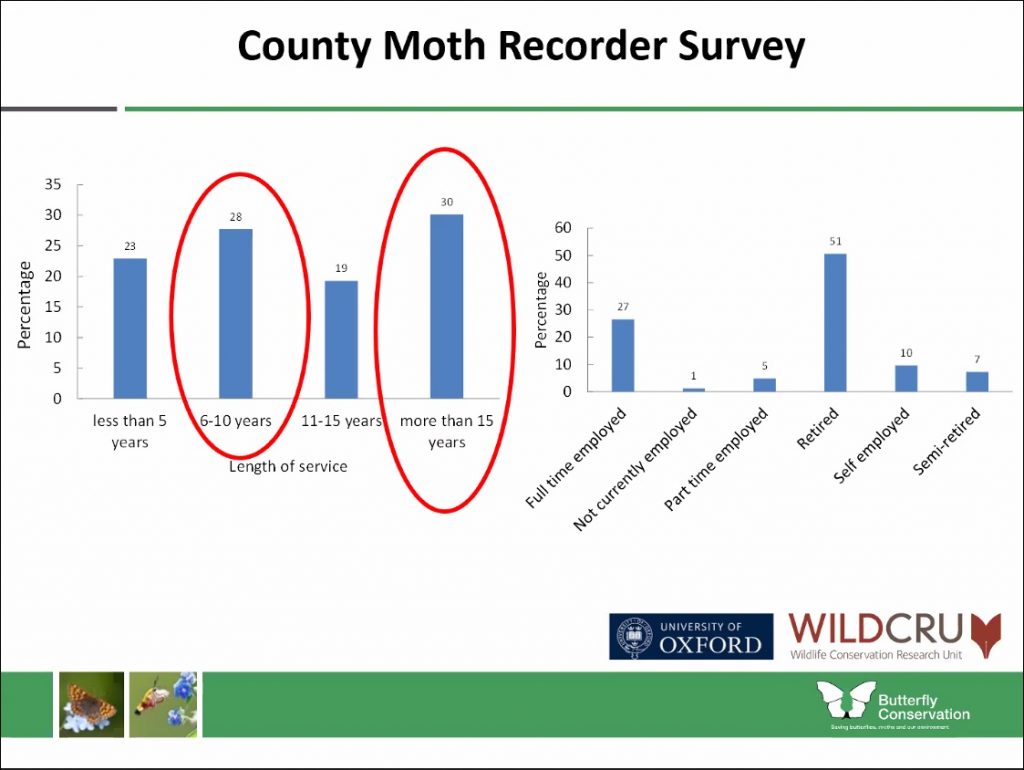
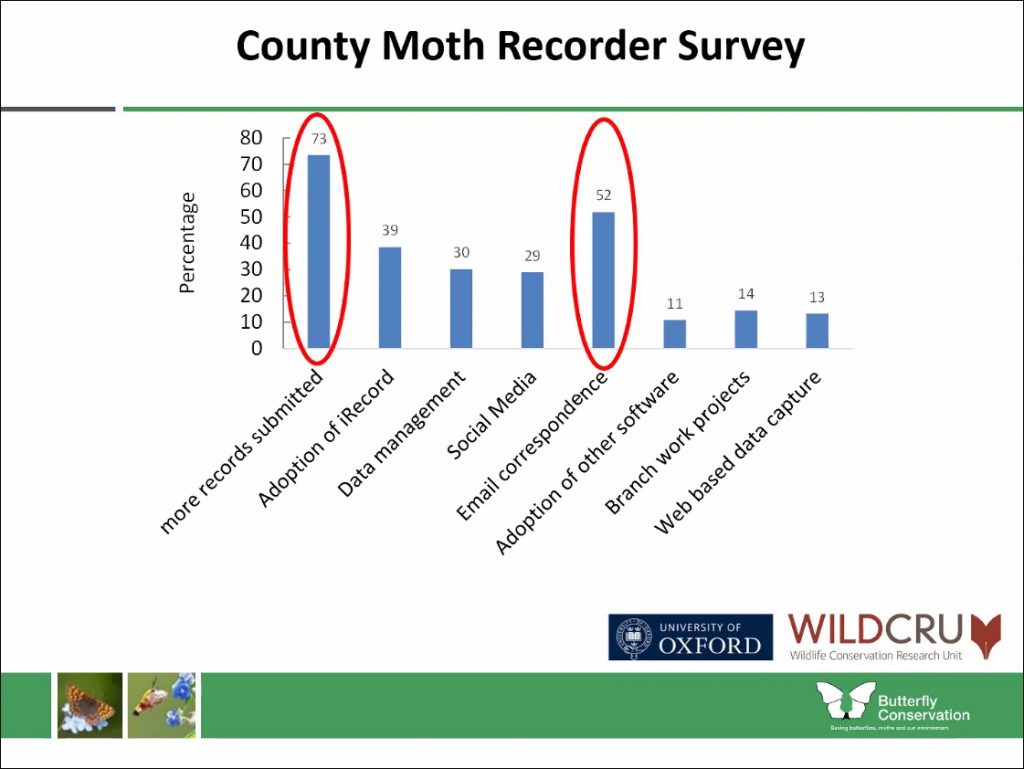
This need to streamline the information in support of county moth recorders was echoed and advanced by Dr. Katie Cruickshanks who was next to speak.
 Katie spoke about the benefits of this widening pool of public participation suggesting that, not only does it expand our understanding of national biodiversity, but it also connects us meaningfully with wildlife and has positive effects on our own personal wellbeing. Public perception of moths and butterflies is improving through events like Butterfly Conservation’s Big Butterfly Count, which encourages people to log the species they see in their local patch for a set period of time using a dedicated app. The wealth of sightings that come through apps like this and iRecord – alongside information gathered from social media and anecdotal sources – has meant that the recording process is a vast and time consuming activity for volunteers. Katie spoke on how this process currently works and speculated on how it might be streamlined moving forwards.
Katie spoke about the benefits of this widening pool of public participation suggesting that, not only does it expand our understanding of national biodiversity, but it also connects us meaningfully with wildlife and has positive effects on our own personal wellbeing. Public perception of moths and butterflies is improving through events like Butterfly Conservation’s Big Butterfly Count, which encourages people to log the species they see in their local patch for a set period of time using a dedicated app. The wealth of sightings that come through apps like this and iRecord – alongside information gathered from social media and anecdotal sources – has meant that the recording process is a vast and time consuming activity for volunteers. Katie spoke on how this process currently works and speculated on how it might be streamlined moving forwards.
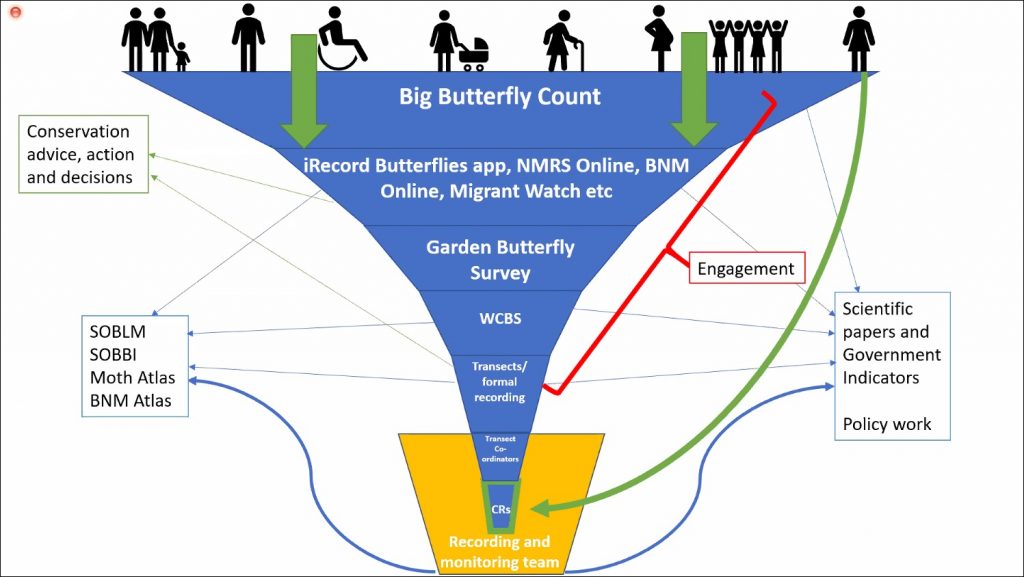
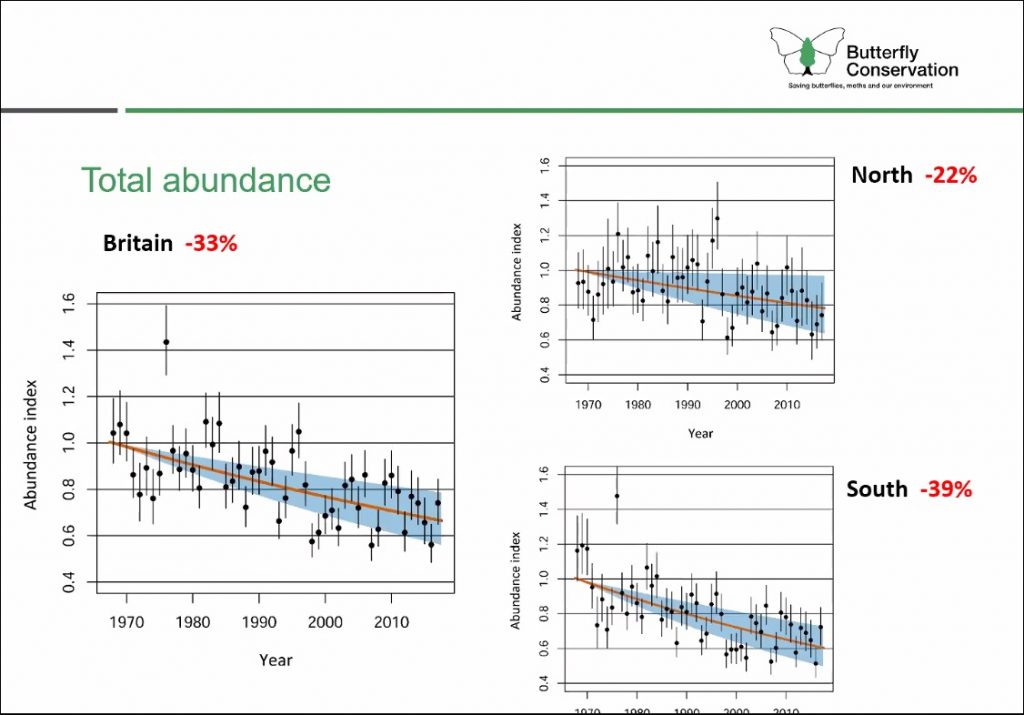
As a follow up to the publication of the Atlas of Britain & Ireland’s Larger Moths at the end of 2019, Dr. Richard Fox spoke next on the state of Britain’s larger moths.
 The compilation of data for the new State of Britain’s Larger Moths 2021 report was an ambitious project and took into account 50 years worth of accumulated information, providing a unique understanding of moth population trends. To date, it represents the longest-running standardised monitoring of insect populations anywhere in the world. The study divides data to create a more accurate picture of the abundance and distribution of larger moths across the country, and takes into account northern and southern records separately to build a stronger idea of where increases and declines in species numbers are occurring. Overall abundance of larger moths caught in traps over the 50 year survey period points to a concerning 33% decline across the country (with a southern decline of 39% and a northern decline of 22%). There is, however, evidence that moth species in the UK have increased their distribution by 9% over a 47 year period (1970-2016).
The compilation of data for the new State of Britain’s Larger Moths 2021 report was an ambitious project and took into account 50 years worth of accumulated information, providing a unique understanding of moth population trends. To date, it represents the longest-running standardised monitoring of insect populations anywhere in the world. The study divides data to create a more accurate picture of the abundance and distribution of larger moths across the country, and takes into account northern and southern records separately to build a stronger idea of where increases and declines in species numbers are occurring. Overall abundance of larger moths caught in traps over the 50 year survey period points to a concerning 33% decline across the country (with a southern decline of 39% and a northern decline of 22%). There is, however, evidence that moth species in the UK have increased their distribution by 9% over a 47 year period (1970-2016).
Dr. Fox also talked through the understanding we now have of distribution indicators for different habitats including woodland, grassland, moorland and heathland. These indicators suggest that “loss and deterioration of wildlife-rich habitats is probably still the main cause of population declines”.
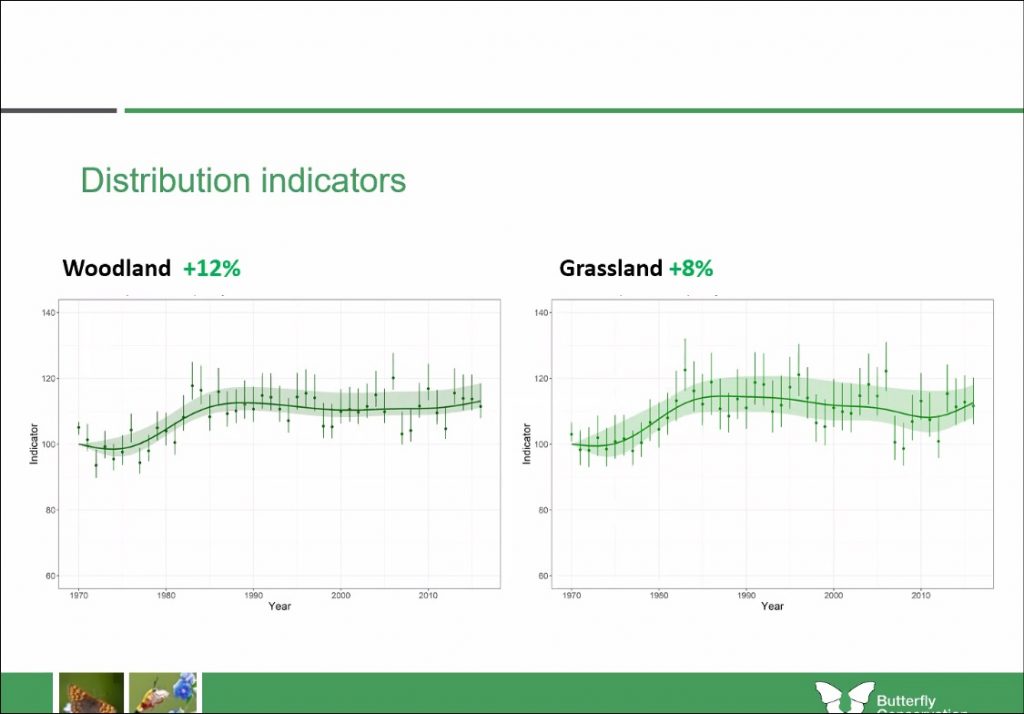
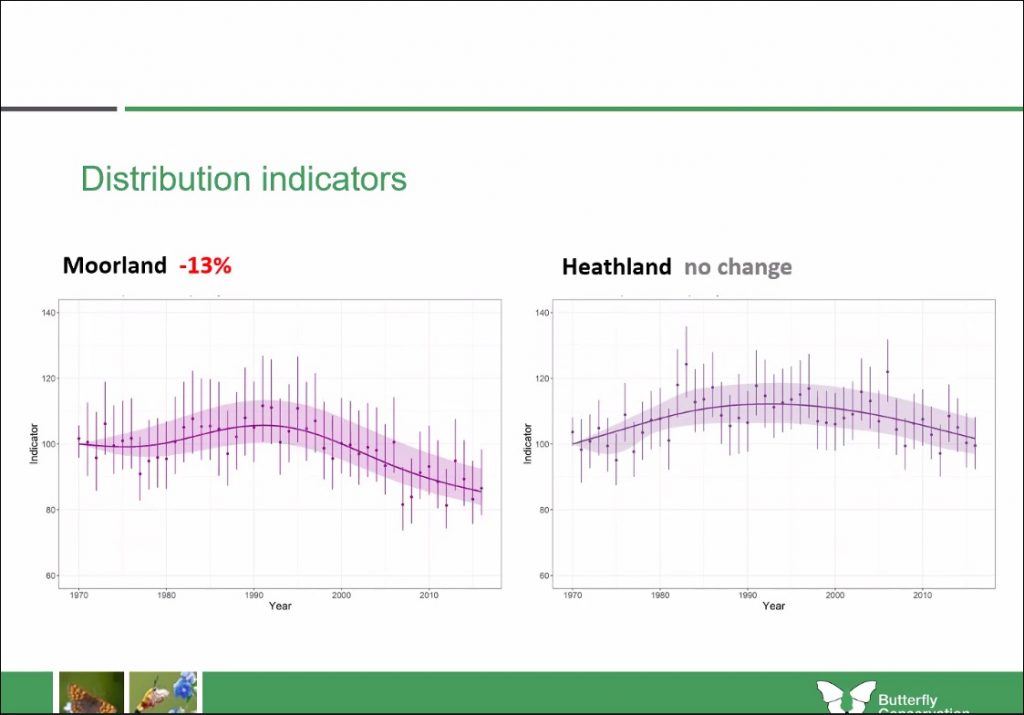
There are, however, many nationwide projects working to correct for this and enrich habitats once again; such as the Highways England roadside verge scheme managed by Butterfly Conservation’s Dr. Phil Sterling, which is working to create improved grassland habitat corridors along roadsides.
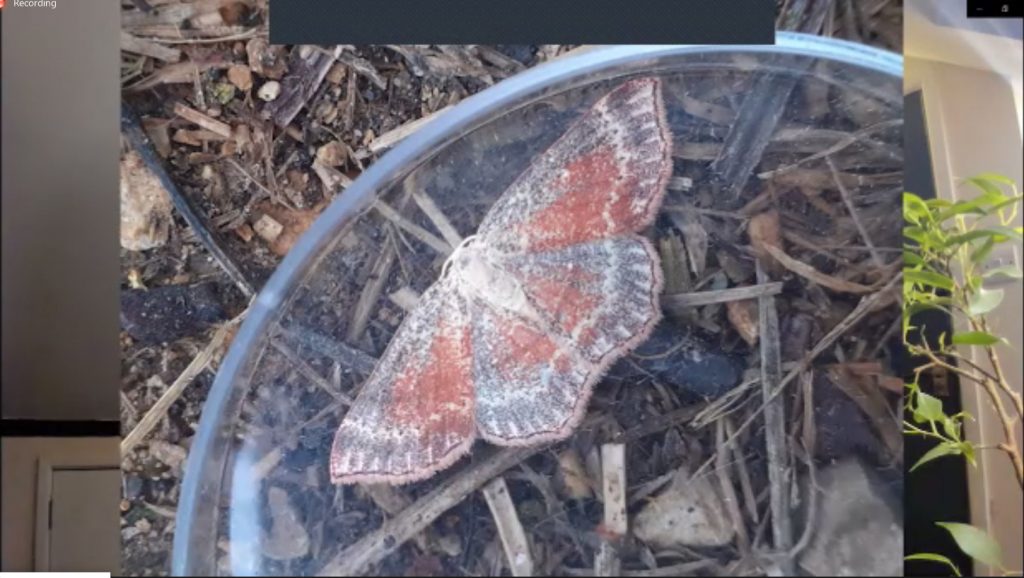
Next came a passionate report on moth trapping through lockdown from Luke Phillips (Dorset RSPB). In this personal account of how national restrictions pushed him to connect more keenly with wildlife locally, Luke described some of the star species that visited his patch throughout the long spring and summer season of 2020, including a scarce Alder Kitten (Furcula bicuspis) and an unusual Birch Mocha variant (Cyclophora albipunctata).


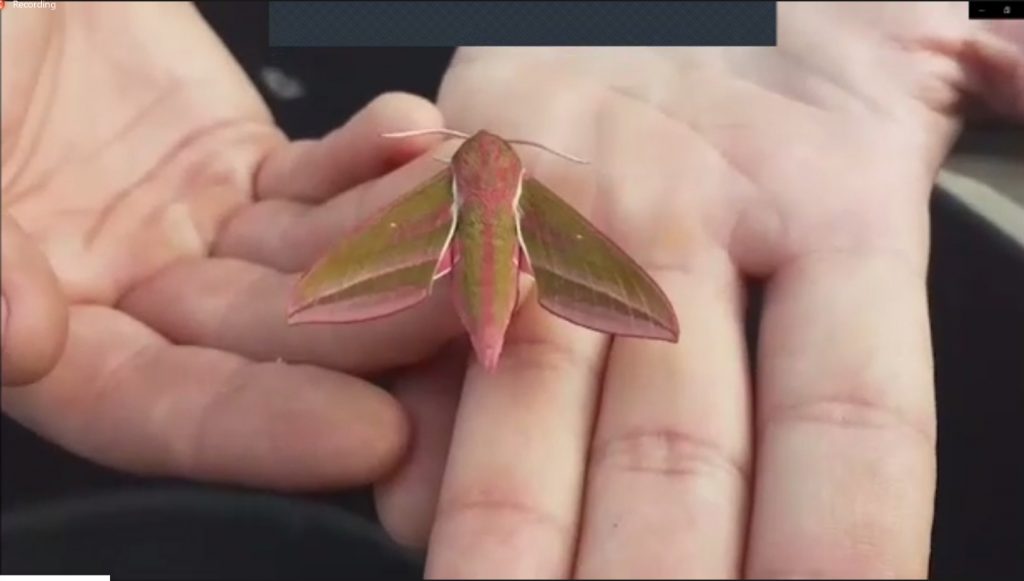
Luke has been involved in a number of public engagement activities that encourage individuals and families to embrace the wildlife in their own spaces, including nationwide moth trap reveals and The Big September Sleepout, which sees hundreds of families across the country meeting to camp in wild places and witness the wildlife around them. In the last year these activities have still occurred, but with participants camping in their own gardens and spaces (in accordance with social distancing measures) and then convening virtually to discuss their findings. The uptake on these activities has been really encouraging and, besides the obvious benefits to wellbeing of connecting people and wildlife in these ways, these moth mornings and camp-outs also produce lots more data for Butterfly Conservation!

The final speaker of the day was Dr. David Wagner, a systematist and lepidopterist from the University of Connecticut, who spoke about Insect Decline in the Anthropocene and How Moths are Faring. David discussed our current understanding of anthropogenic impacts on climate through habitat destruction and the intensification of agricultural practices around the world, and how their knock-on effects impact on parts of the tropics that are still feeling little to no direct harm from these practices. As a result of spreading drought conditions through the world’s grasslands and cloud bank diminishment in the tropics it is clear that insect abundance is in decline (although some species are faring better than others, and even increasing in numbers).
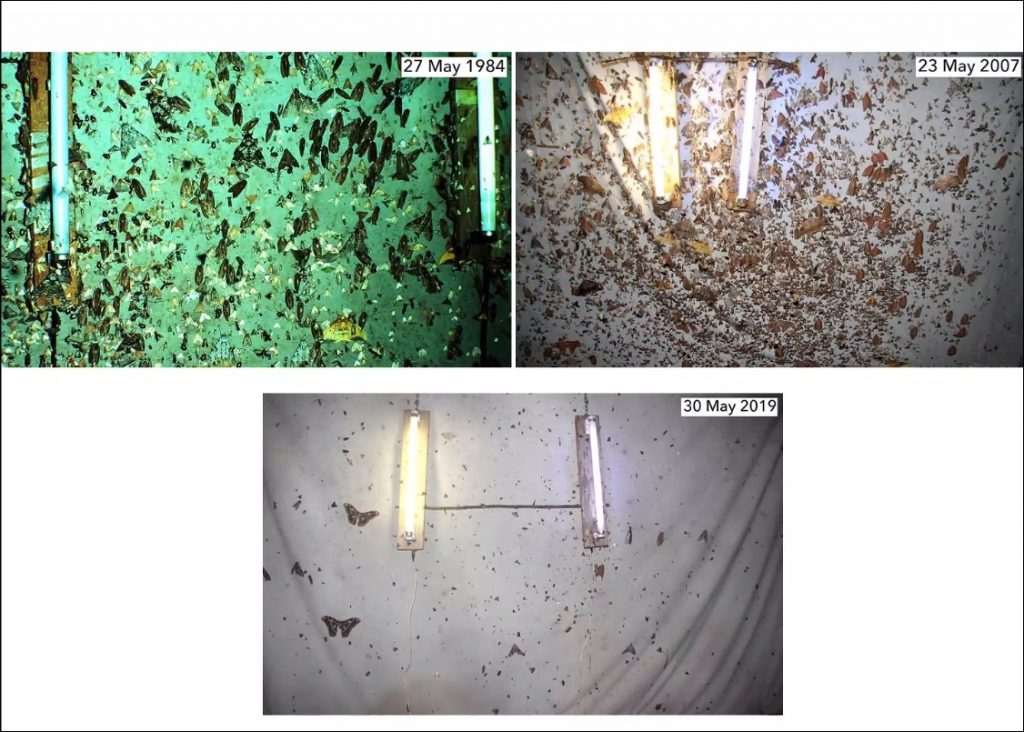
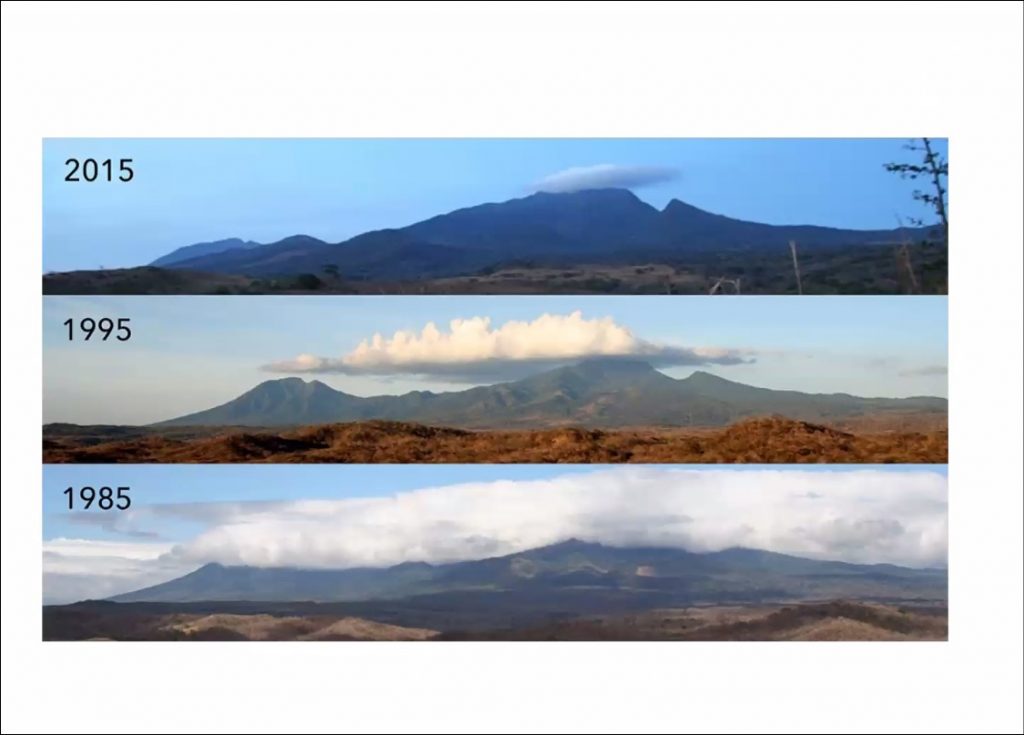


David pointed out that the most concerning thing is situations where there are declines in common/abundant species in parts of the world where there is little to no anthropogenic impact. This indicates a systemic problem that we can’t yet see. But in the unique case of the United Kingdom, where we have a vast archive of data collection and large levels of public involvement in monitoring, we can see more clearly the impacts of emerging anthropogenic factors, and this can inform our understanding to a certain degree. This depth of research has still not been realised in most parts of the world which means our global view of how insect populations at large are faring is incomplete.

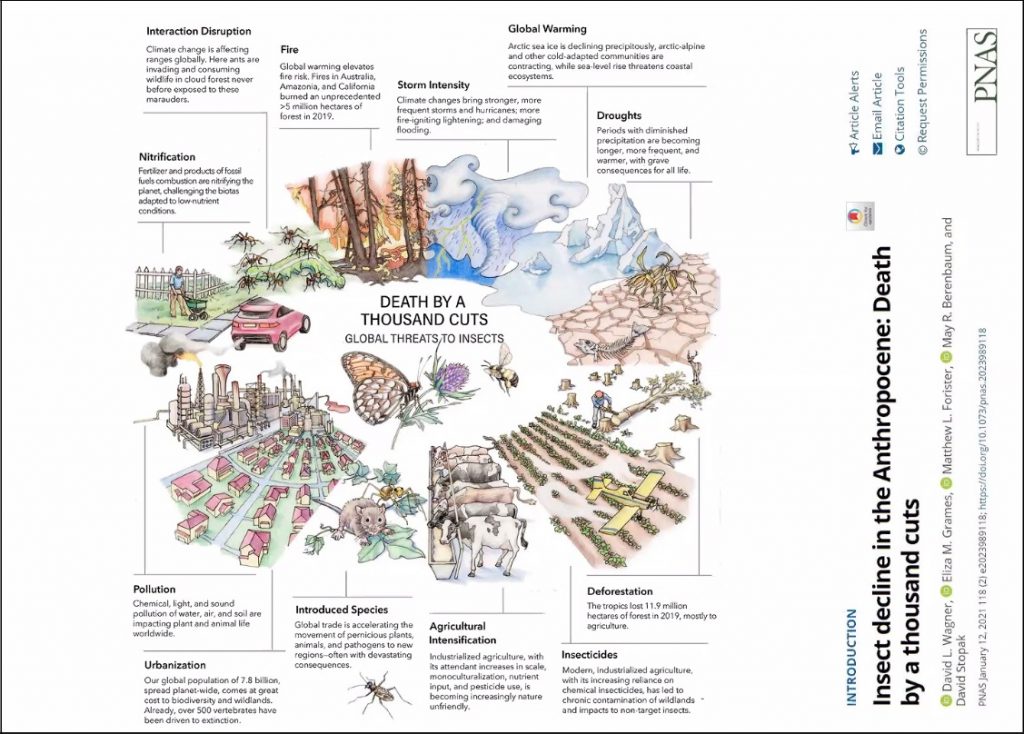
The morning wound up with an important message to anyone passionate about moth and insect conservation: keep working at collecting the data, keep submitting records, lend your voice as an ambassador for insect surveying where you can, and continue to learn and encourage learning.

If you would like to get involved in future talks or events with Butterfly Conservation, you can find out more on their website.






