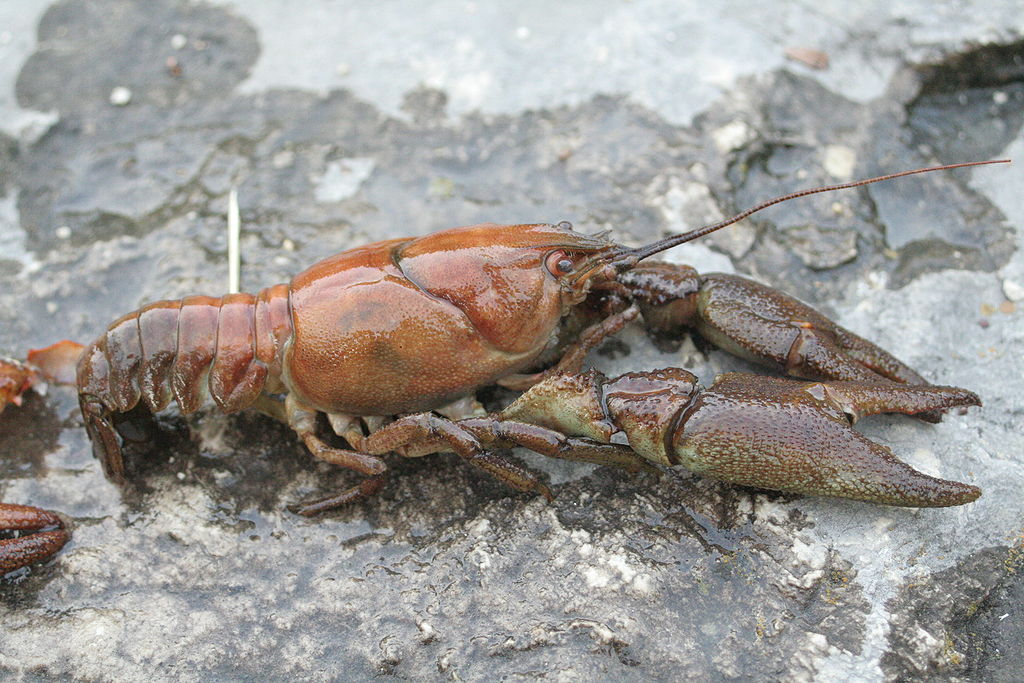
The UK is home to a single native species of crayfish – the white-clawed crayfish Austropotamobius pallipes. This attractive freshwater crustacean has a bronze-coloured body and white-undersides to its claws, for which it is named. They require clean freshwater habitats such as streams, rivers and lakes where they can rest under stones and rocks during the day and then spend the night foraging for food. Their diet is omnivorous and they feed on a range of foods including plants, carrion and invertebrates. They will also eat other white-clawed crayfish when the opportunity arises!

Threats to native UK crayfish
The white-clawed crayfish was once widespread and common throughout England and Wales, but since the 1970s populations have declined by 50–80%. Without intervention it is expected that they will become extinct over the next 20 years. Their decline is in large part due to the introduction of the North American signal crayfish which outcompetes the native crayfish for food and habitat. The signal crayfish also carries ‘crayfish plague’, a fungal disease that the white-clawed crayfish has no natural resistance to. Declining water quality and loss of suitable freshwater habitats have also contributed to their decline.
How are crayfish protected in the UK?
White-clawed crayfish are fully protected under the Wildlife and Countryside Act 1981 and The Conservation of Habitats and Species Regulations (2017). As a result, it is an offence to kill, injure or disturb them and their habitat cannot be destroyed or damaged. Any development which will, or is likely to, impact white-clawed crayfish and their habitat will only be allowed if it provides a net benefit to the crayfish through a combination of mitigation, compensation and enhancement strategies. This may involve habitat restoration projects or the modification of existing freshwater areas to make them more suitable for crayfish to survive and thrive.
When and how are crayfish surveyed?
Crayfish surveys are required if a development is being planned in an area that currently supports, or has the potential to support, white-clawed crayfish. They can be surveyed using a variety of methods including relatively new eDNA technology, which analyses water samples to detect the presence of DNA specific to the white-clawed crayfish. eDNA studies, however, cannot provide information on population size and so follow-up surveys are usually required should eDNA be detected. Most commonly crayfish are surveyed by manually searching likely refuges. If this isn’t possible due to access issues or water depth then crayfish traps can be deployed. These traps are of the live-catch variety – trapped individuals are returned to the water unharmed once they have been recorded.
What else is being done to conserve the white-clawed crayfish?
As well as being afforded a high level of protection in UK legislation, there are a number of conservation projects which aim to conserve or bolster existing populations of white-clawed crayfish. As part of the South West Crayfish Project, Bristol Zoo are breeding white-clawed crayfish in captivity which can be used to boost existing populations or establish new ones. They are also valuable in educating zoo visitors about their plight.
Control of introduced crayfish is also being carried out in certain areas through trapping or the use of biocides. Similarly, the control of plague and other crayfish diseases is of paramount importance. All waterway users should be aware of how easily plague spores are carried between sites and make all reasonable efforts to stop it spreading via their clothes and equipment. Download the Crayfish in Crisis information sheet for more information.
Recommended reading and equipment
Full of guidance and practical advice, this large, full-colour manual is the first conservation handbook for England’s crayfish. This manual provides best practice advice and guidance in one easy-to-follow publication, with references, case studies and examples.
 Management of Freshwater Biodiversity: Crayfish as Bioindicators
Management of Freshwater Biodiversity: Crayfish as Bioindicators
Integrating research into freshwater biodiversity and the role of keystone species, this fascinating book presents freshwater crayfish as representatives of human-exacerbated threats to biodiversity and conservation.
This robust all-plastic crayfish trap is very easy to handle and quick to set and re-bait.
 Aluminium Crayfish Refuge Trap
Aluminium Crayfish Refuge Trap
This simple refuge trap is safe for use where water voles and otters are present.
 Snowbee Granite PVC Chest Waders
Snowbee Granite PVC Chest Waders
Snowbee Granite waders are manufactured from a heavy-duty, reinforced laminate PVC which is extremely tough and hard-wearing while also being soft and flexible for ease of movement.