Deer are among the UK’s most elegant and familiar mammals and sightings of them in their natural habitat are always special moments, however these encounters can often be fleeting, and our views obscured.
This ID guide covers all of the native and non-native deer species that are found in the UK, and describes the key features to look out for to aid in their identification.
Deer are hoofed ruminants that comprise the family Cervidae. They are naturally found across Europe, Asia and the Americas and can be divided into two subfamilies, differentiated mostly by their bone structures. Most familiar in the UK are the Cervinae or old world deer subfamily, which includes the red, sika, fallow, Chinese water and Reeves’ muntjac. The Capreolinae (new world) sub family includes the roe deer as well as elk, reindeer and all the species found across the Americas.
Of the six species found in the UK, only the red and roe deer are truly native, although fallow deer were thought to have been first introduced to Britain in the 11th Century from the Mediterranean region, so are long established. Three other species, the sika deer, Chinese water deer and Reeves’ muntjac are all more recently naturalised within the UK.
Identification of deer can be straightforward in some situations, but some species are similar and, when not seen well, identification can be a challenge. Two of the best features to focus on for identification are the rump and the antlers, if they are visible. Except for reindeer (caribou), in which both sexes grow antlers, and the Chinese water deer and musk deer, which lack any antlers, all male (stags) deer usually grow antlers, which they use in battles to access females (hinds) during the rut. Antlers are unique to deer and a great tool to look at to identify different species. However, they are shed every year after the rut, so although a striking feature, the rump pattern of deer is perhaps the most reliable feature to use for identification.
Red Deer (Cervus elaphus)

Distribution: Widespread in Scotland and abundant in the Highlands and Islands. Elsewhere populations occur in Cumbria, Lancashire, the Peak District and Pennines, Exmoor and the Quantock Hills, the New Forest, and East Anglia. There are also small populations in Wales and Ireland.
Head and body length: 1.6–2.6 metres for a male and 1.7–2.1 metres for females
Height at shoulder: 1.14–1.22 metres.
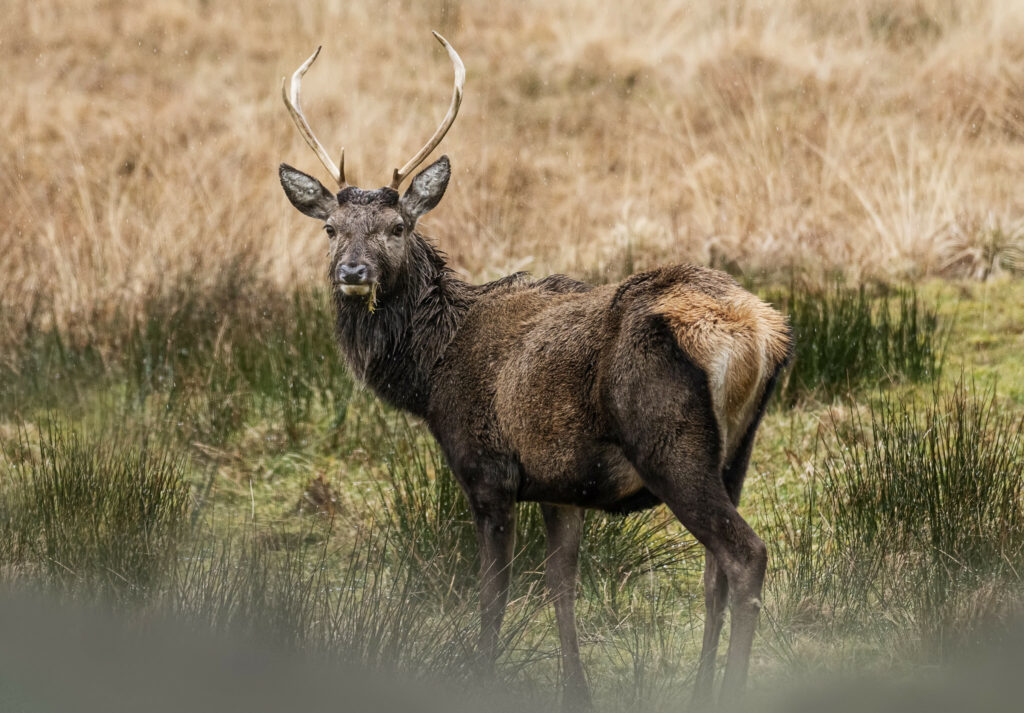
What to look for: Both our largest species of deer and land mammal, the magnificent stags can weigh in at around 200kg making them an impressive and noticeably large species. Look for their reddish-brown coat that lacks any spots or delineation of colour. Only their rumps and tails feature a paler buff cream colour. Another characteristic of red deer are their elongated faces and large ears.
Their favoured habitat is woodland, although in Scotland they have adapted to live year-round in more open treeless landscapes. Grasses make up the bulk of their diet throughout the year, but they will also browse on a wide range of shrubs, young trees and bark, brambles, bracken and heathers. Sika deer are the most similar looking and the two species have hybridised in several regions. Sika have white spots in summer and darker brown coats in winter with shorter faces. Hybrid red and sika deer tend to resemble smaller darker red deer than they do sika.
Antlers: The antlers of mature stags are wide and branching with usually 8 sets of points per antler that curve upwards and sometimes in on themselves. Younger males have short unbranched, straighter pointed antlers.
Rump: A soft creamy colour with a very short russet-brown tail.
Sika Deer (Cervus nippon)

Distribution: Sika deer are native to Japan, Korea, Taiwan and far eastern Asia, but escaped into Britain from collections in 1860. Since their initial introduction in 1860, they have naturalised and spread to many regions. Population strongholds include Dorset and the New Forest, Lancashire and Cumbria Northern England, the Scottish borders and the Highlands.
Due to their genetic similarities to red deer, sika deer are thought to have hybridised with the native red deer in several regions, particularly in the Scottish Highlands. Sika prefer to keep to woodland cover more than red deer which have adapted to feeding in more open habitats.
Head and body length: 1.2–1.9 metres for a male and 1.1–1.6 metres for female.
Height at shoulder: 1.07–1.22 metres.
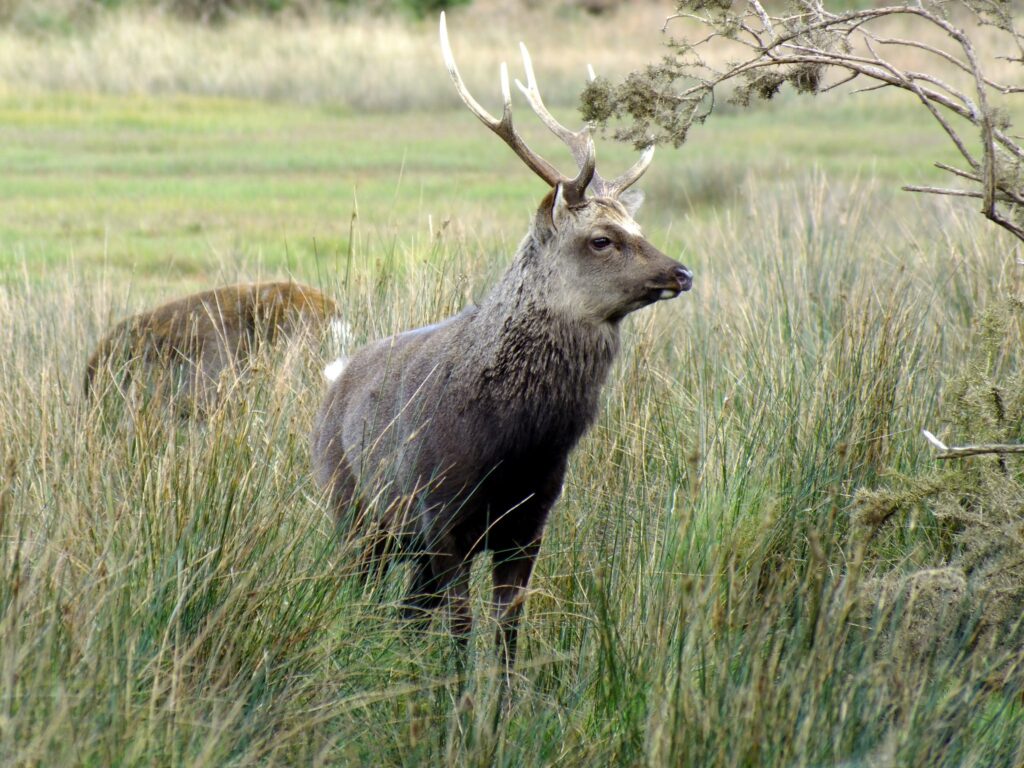
What to look for: Sika are very similar in appearance to red deer and the two species do interbreed in many regions. They are noticeably smaller than red deer and in summer they have white spots on their coats, but thick and often dark (sometimes almost black) coats in winter.
Their diet and feeding habits are very similar to red deer, with grasses and heather making up the bulk of their diet, but they will also browse on both deciduous and coniferous trees, gorse, holly bark and acorns. They are however generally less social than red deer and outside of the breeding season, both males and females can be solitary with females forming only small herds with young.
Antlers: Similar to those of red deer, but thinner, lighter coloured and less complex with usually only 4 points per antler.
Rump: A conspicuous white rump patch with a dark edge and a short white tail with a single thin dark dorsal stripe along its length.
Roe deer (Capreolus capreolus)

Distribution: A woodland specialist that’s rarely found far from some woodland cover, although they are increasingly using hedgerows and scrub as cover within more agricultural and urban landscapes. They are widely distributed throughout the UK but absent from Ireland, with the greatest population densities found in Scotland.
Head and body length: 0.95–1.25 metres
Height at shoulder: 0.6–0.75 metres
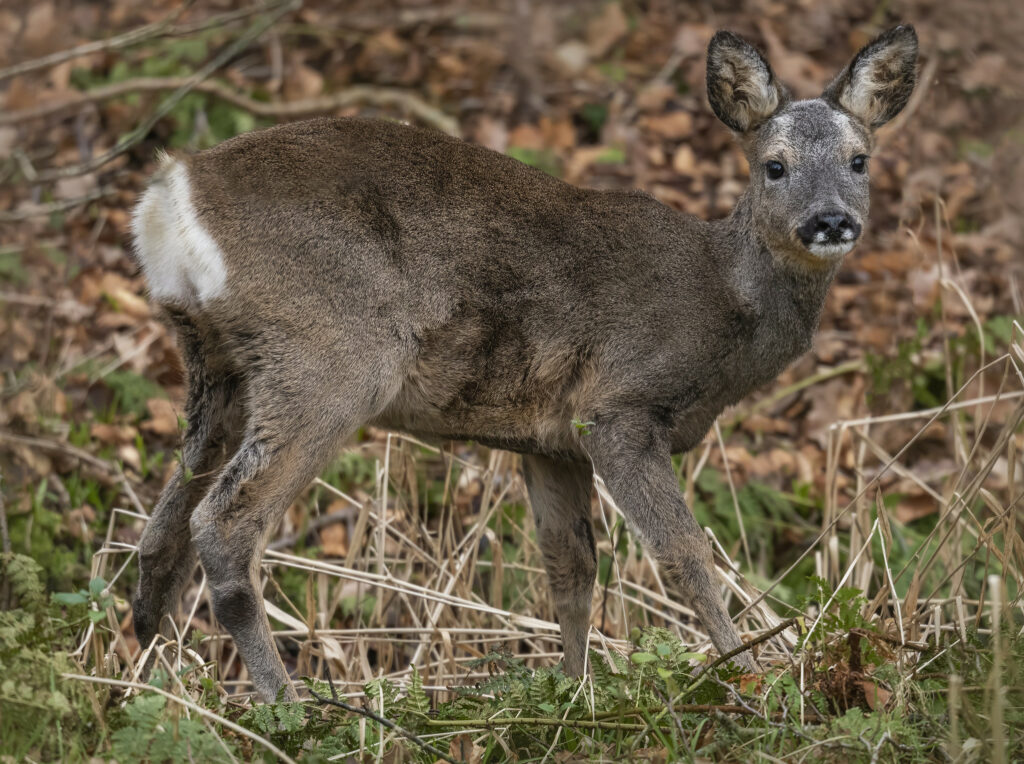
What to look for: A medium sized lightweight deer with a long neck and uniform brown coat. Other features that distinguish them from the larger deer include shorter muzzles and a clean white rump patch. In summer their coats turn a rich reddish brown and appear sleeker, while in winter, the coat turns a thicker and dark more peanut brown.
They are mostly solitary but sometimes form small family groups with young, particularly during the winter. They browse a wide variety of trees, shrubs and herbs including bramble, heather, and rosebay willowherb but during the autumn will also feed on the ground on fruits, acorns and occasionally fungi.
Antlers: Short and mostly vertical, they are rarely much taller than the head, with only 2 or three points per antler. With a close view, the antlers can often appear particularly velvety or crusty at the base, depending on the season and growth stage.
Rump: The patch varies between the sexes, but both have a clean white patch and no visible tail. Males have a kidney shaped white patch, whereas females have more of a round shape.
Chinese water deer (Hydropotes inermis)
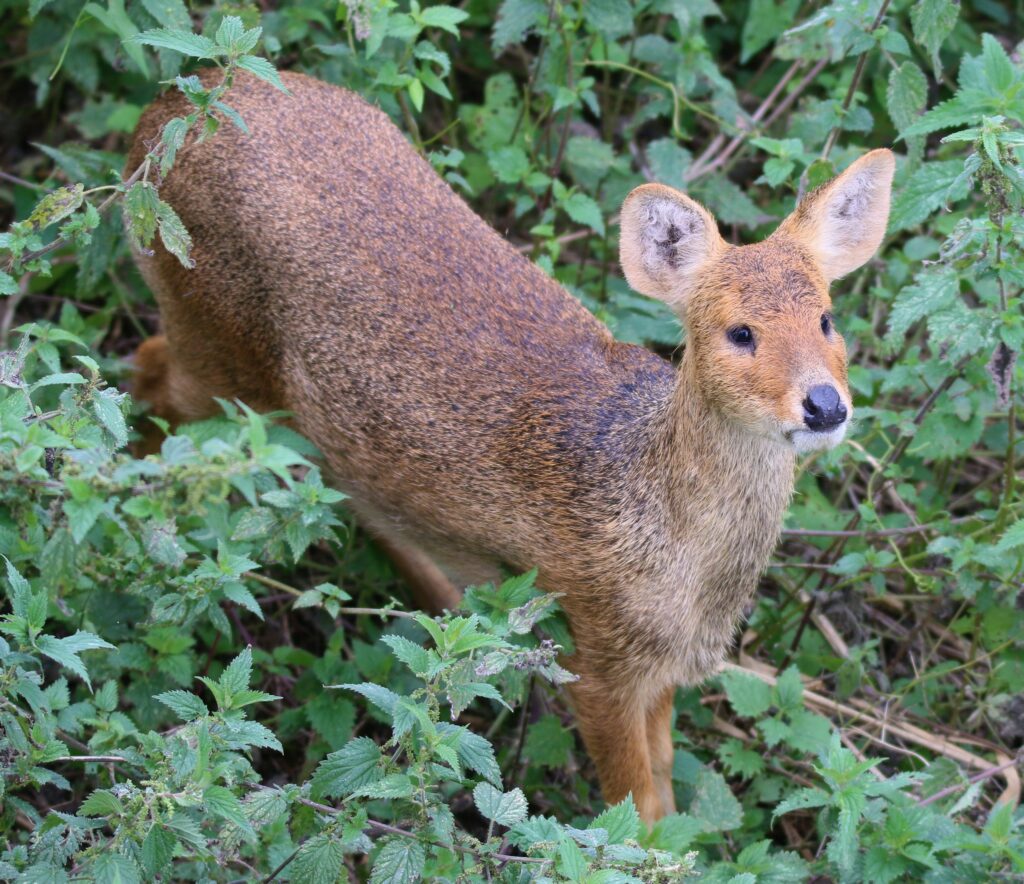

Distribution: The Chinese water deer is a native of eastern China and Korea but has formed a naturalised population in England after escaping from Woburn Park in Bedfordshire towards the end of the 19th Century. They’re found throughout most of East Anglia and a more scattered population in the southeast-England where there is suitable habitat. The strongholds include the Norfolk broads and Cambridgeshire fens. The population trend is increasing, with over 1500 individuals and their distribution is also expanding. Interestingly, it is thought that due to population decline in their native range, the British population may now represent a significant part of their world population, despite not being a native species.
Head and body length: 1 metre
Height at shoulder: 0.7–0.95 metres.
What to look for: A small and uniformly light brown (sometimes greyish) coloured deer with large, rounded ears and a distinctive black nose. They are strongly associated with freshwater marshland habitats where they feed on coarse grasses, reeds, herbs and aquatic vegetation. Chinese water deer are solitary and secretive, preferring to keep close to cover and use both woodland close to wetlands and reedbeds. They will occasionally forage in farmland but prefer to keep close to cover.

Males have impressive and prominent downward pointing tusks instead of canine teeth that can be seen with a close-up view. These tusks are used during the rut, mostly for display purposes between rival males and to impress females. They are quite a distinctive looking deer with a more unusual almost bear-like face, although their secretive nature means that obtaining good views can be difficult.
Antlers: This species lacks any antlers.
Rump: Their rear and short tail is the same pale brown colour as the rest of their coat.
Reeves’ muntjac (Muntiacus reevesi)
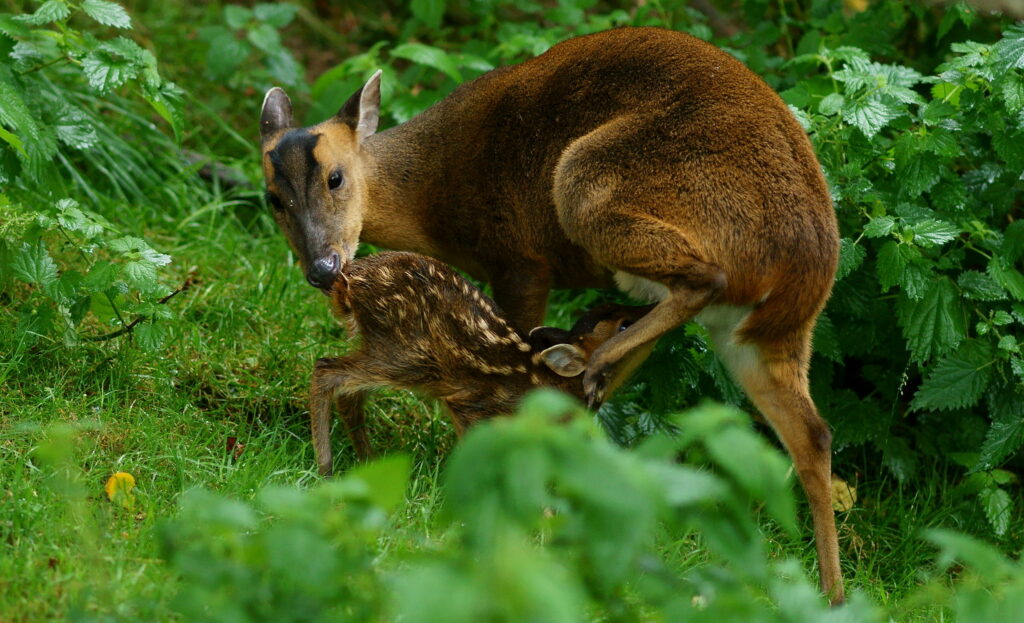

Distribution: The Reeves’ muntjac is also native to China and again its UK population derives from escaped individuals from Woburn Park in Bedfordshire from 1901. They are now abundant and found throughout southern, eastern and central England spreading rapidly into southwest-England, Wales and southern Scotland. Since 2000, a population has become established in Ireland and Northern Ireland.
Head and body length: 0.9–1 metres
Height at shoulder: 0.45–0.52 metres
What to look for: A very small, robust and stocky deer that often appears to have a hunched-over appearance due to its short neck, arched back and tendency to walk with its head facing down to the ground. The coat varies from a deep russet brown in summer to a greyer and paler brown in the winter. The face is short and squat with a characteristic set of black stripes creating a V shape on the top of the head. Male muntjac also have slightly protruding tusks but they are much shorter than those of Chinese water deer and rarely visible without a close view.
Muntjac favour dense undergrowth within both deciduous and coniferous woodland but will also thrive within urban environments with suitable cover. They browse woodland leaves and flowers during the spring and summer including some scarce woodland ground flora species. During the autumn and winter their diet switches to nuts, fungi and grasses.
Antlers: A single very short point that curves back.
Rump: The rear patch and tail are the same reddish-brown colour as the back. The tail is short but when alarmed it will often raise the tail revealing the white underside.
Fallow Deer (Dama dama)
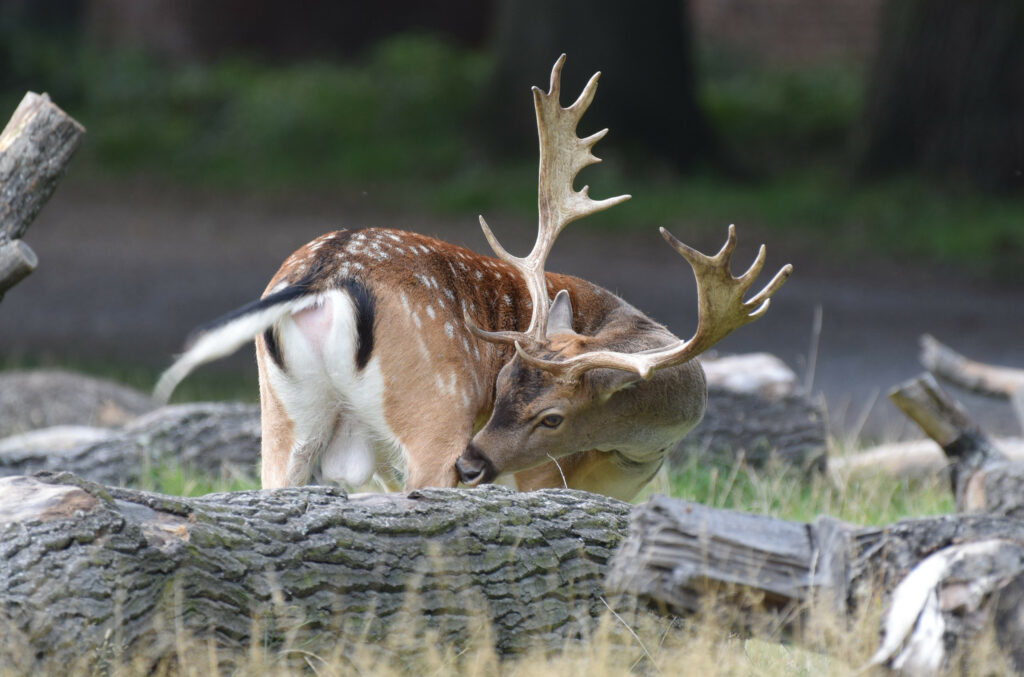
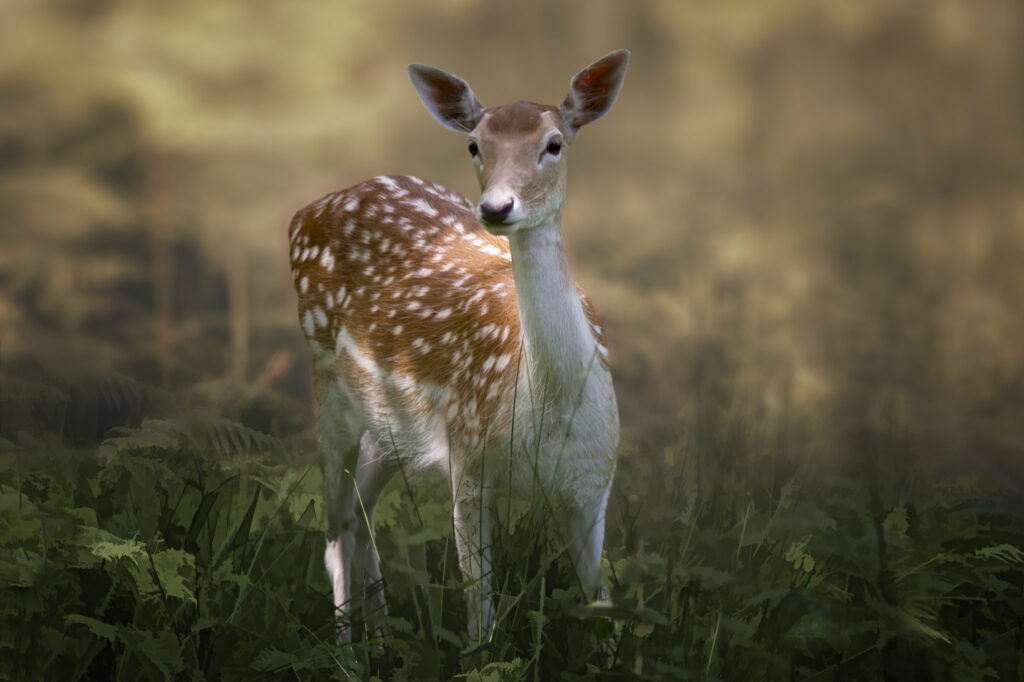


Distribution: Introduced to Britain for hunting in the 11th Century and to Ireland in the 13th Century from the Eastern Mediterranean, the species is now found throughout England, with more scattered populations in Wales and Scotland.
Head and body length: 1.45–1.55 metres for a male and 1.30–1.45 metres for a female.
Height at shoulder: 0.7–0.95 metres
What to look for: Fallow deer are quite variable in their appearance due to their wide range of pelage (hair). Typically, most individuals have some conspicuous white spots on pale brown, fawn or gingery coats in the summer and then dark brown coats with only faint or no spots in the winter. There is a great range of variation within this species though with some individuals and populations remaining very dark or very pale throughout the year, some of which can be melanistic. Fallow are medium sized deer that are very social, often forming large herds that remain together throughout the year. Due to their numbers, they also leave conspicuous signs of their presence such as runs and tracks in frequented areas.
Their preferred habitat is open deciduous woodland but will also use farmland and woodland edge habits if there is cover close by. Fallow deer are grazers with grass forming most of their diet, although they will also eat nuts and browse on heather, holly and some deciduous trees to a lesser extent.
Antlers: Very large, broad and palmate shaped with numerous spikes.
Rump: A clean white rump with a dark outside edge. The tail is long and appears mostly black because of a long black stripe that runs down the course of its length, but the underside is clean white.
Further Reading:
 Britain’s Mammals: A Field Guide to the Mammals of Great Britain and Ireland
Britain’s Mammals: A Field Guide to the Mammals of Great Britain and Ireland
£17.99
 How to Find and Identify Mammals [Revised Edition]
How to Find and Identify Mammals [Revised Edition]
£11.99
Mammals of the British Isles: Handbook
£34.99
A Guide to British Mammal Tracks and Signs
£3.75
£4.99
£4.99
 Scottish Red Deer and Their Conservation
Scottish Red Deer and Their Conservation
£27.99
£22.95
 Muntjac and Water Deer: Natural History, Environmental Impact and Management
Muntjac and Water Deer: Natural History, Environmental Impact and Management
£34.99
All prices correct at the time of this article’s publication.