Rabbits and hares are species in the family Leporidae, which contains over 60 species. They are mammals within the order Lagomorpha, together with the pikas. They are small to moderate-sized species, characterised by long hind legs, long ears and rapid movements. They are almost exclusively herbivorous, feeding mainly on grasses and herbs, although they do also eat leaves, fruits and seeds. Leporids are coprophagous, meaning they pass food through their digestive system twice. To do this, they first expel the food as soft green faeces, termed cecotropes, which they then reingest, eventually expelling it again as dark faecal pellets. This increases their ability to break down and digest plant material, extracting further nutrients.
They inhabit a wide range of habitats, from mountains and wetlands to forests and grasslands. Leporids play an essential role in many of these ecosystems, as seed dispersers, ecosystem engineers (a species that significantly modifies their environment) and as a primary prey item for a number of predator species, such as foxes, wildcats and some mustelids, including stoats and weasels. Their young are particularly vulnerable to these predators, as well as badgers, domestic cats and several birds of prey. Because of this vulnerability, many leporids have large litters, often nesting in burrows underground to protect their young from predation.
One threat to populations, particularly in European rabbits, is myxomatosis, a disease caused by the poxvirus Myxoma virus. Its two natural hosts, the tapeti and brush rabbits of South, Central and North America, experience only mild disease. However, myxomatosis is a severe and usually fatal disease in European rabbits. When the disease originally spread to the UK in the early 1950s, the mortality rate was 99%. In the 1970s this declined to between 47 and 69% but populations were severely affected. The disease, which causes localised swelling, skin lesions, blindness and respiratory distress, has also been deliberately introduced into the wild on multiple occasions. Used to try to eradicate or control rabbit pest populations, myxomatosis was intentionally introduced in Australia, New Zealand, South America and parts of Europe, including Britain.
Other threats to leporid populations include rabbit haemorrhagic disease (RHDV1 and RHDV2), hunting, habitat loss and agricultural intensification. Rabbit populations declined by 64% in the UK between 1996 and 2018 and numbers of brown, mountain and Irish hares are also thought to have declined in some areas. As ecosystem engineers, the loss or reduction of these species can have major consequences, particularly for rabbit-dependent habitats. In their absence, the consequent changes in vegetation structure due to a lack of grazing can have further impacts on other wildlife, such as invertebrates.
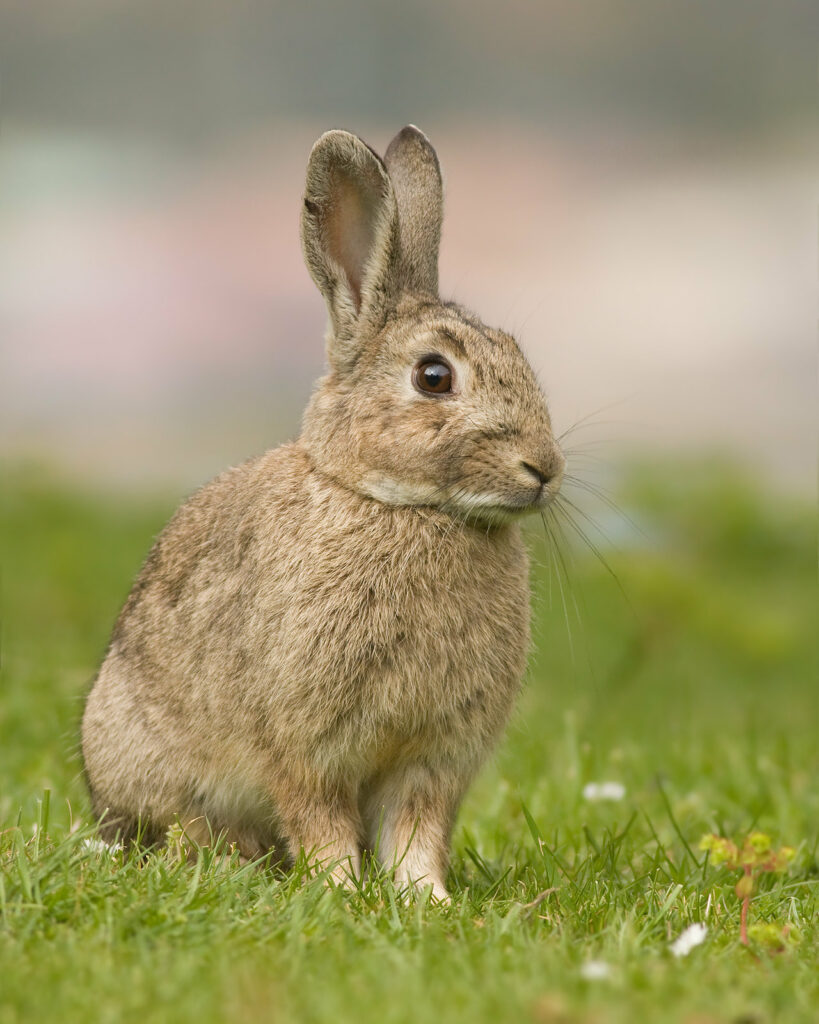
Rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus)
Distribution: Widespread across the UK, although they are absent from Rum, Isles of Scilly and some smaller islands.
What to look for: Rabbits are the smallest leporids in the UK, with the characteristic long ears and long hind legs. They have a sandy, grey-brown colouration and a white tail. They have dark, amber coloured eyes. Other than their size, the most noticeable difference between rabbits and other leporids in the UK is the lack of a black tip on the ears.
Did you know? The rabbit, also known as a coney, is not native to the UK. The exact date of their introduction is one of ongoing research. It was previously thought that rabbits were first introduced by the Normans in the 11th or 12th century as both a food and fur resource. But the recent re-examination and radiocarbon dating of a bone found at a Roman palace show that at least one rabbit was present much earlier, in the first century AD. Researchers have stated that there is no evidence of many rabbits in the area and another analysis suggests the rabbit was kept in confinement, therefore it has been suggested that it was most likely kept as an exotic pet.

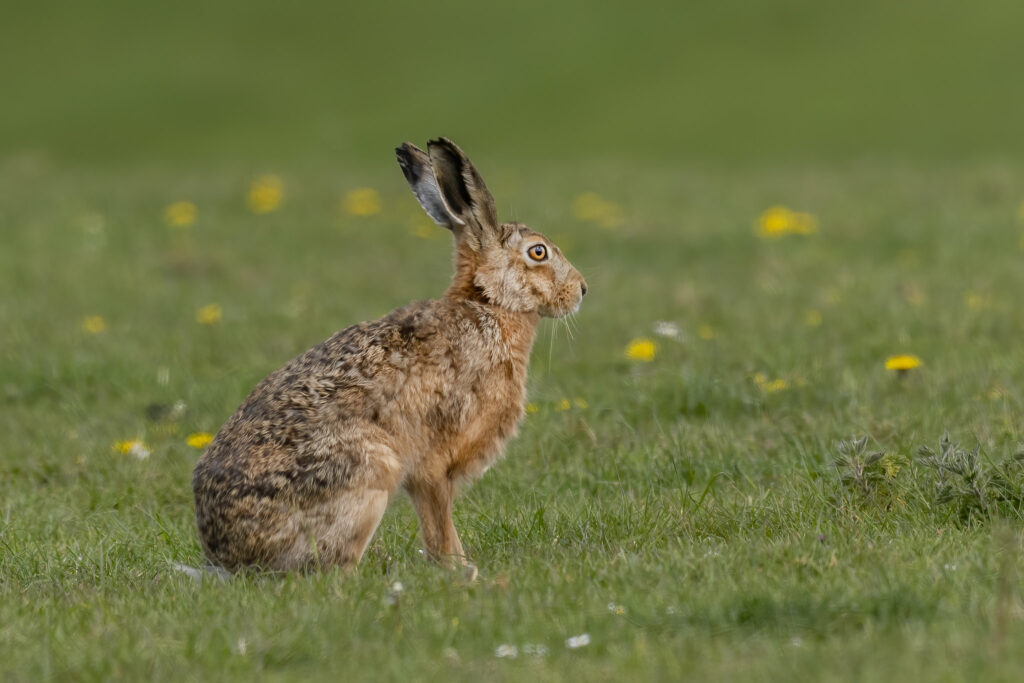
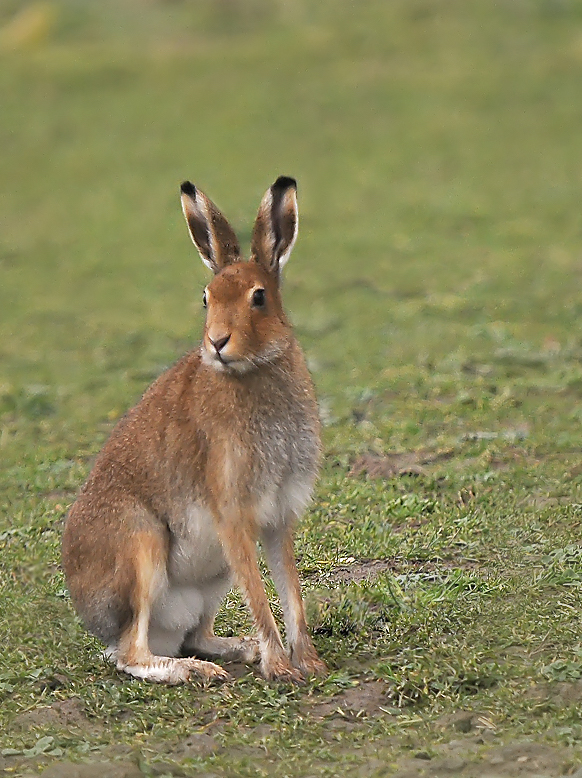
Brown hare (Lepus eueopaeus)
Distribution: Widespread across the UK, although they are less common and more restricted in Northern Ireland and absent from parts of north-west Scotland.
What to look for: This species is larger than the rabbit, with long, black-tipped ears and very long hind legs. Their colouration is redder than the rabbit and the mountain hare, and they have a black-topped tail that is white underneath. The brown hare has amber eyes and their fur can appear grizzled.
Did you know? This species is also non-native and were introduced in the Iron Age. Radiocarbon dating of bones found in Hampshire and Hertfordshire, along with historical accounts, suggest that brown hare were not eaten until hundreds of years later during the Roman period, and were instead associated with deities.

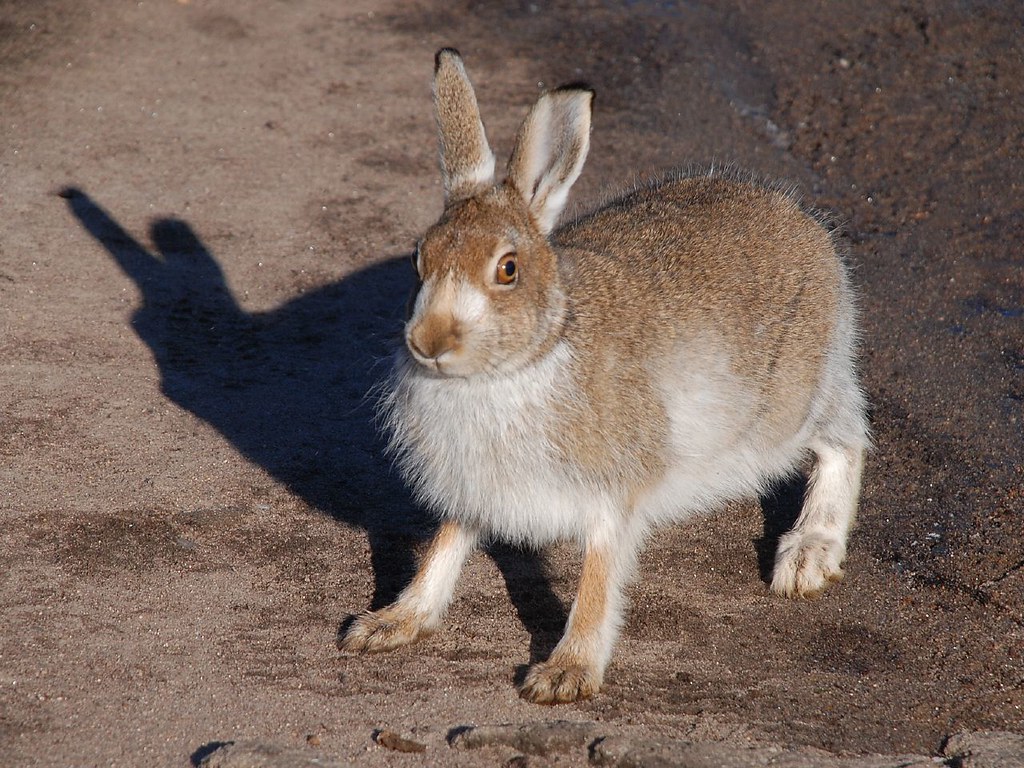
Mountain hare (Lepus timidus)
Distribution: Mainly in the highlands of Scotland, although they are also found in other areas of Scotland, on some Scottish islands and in the Peak District.
What to look for: This species has a grey-brown coat during the summer and a white coat in the winter, although the tips of their ears remain black in both forms and their tail remains white. They have brown eyes and long ears, although these are shorter than the brown hare’s.
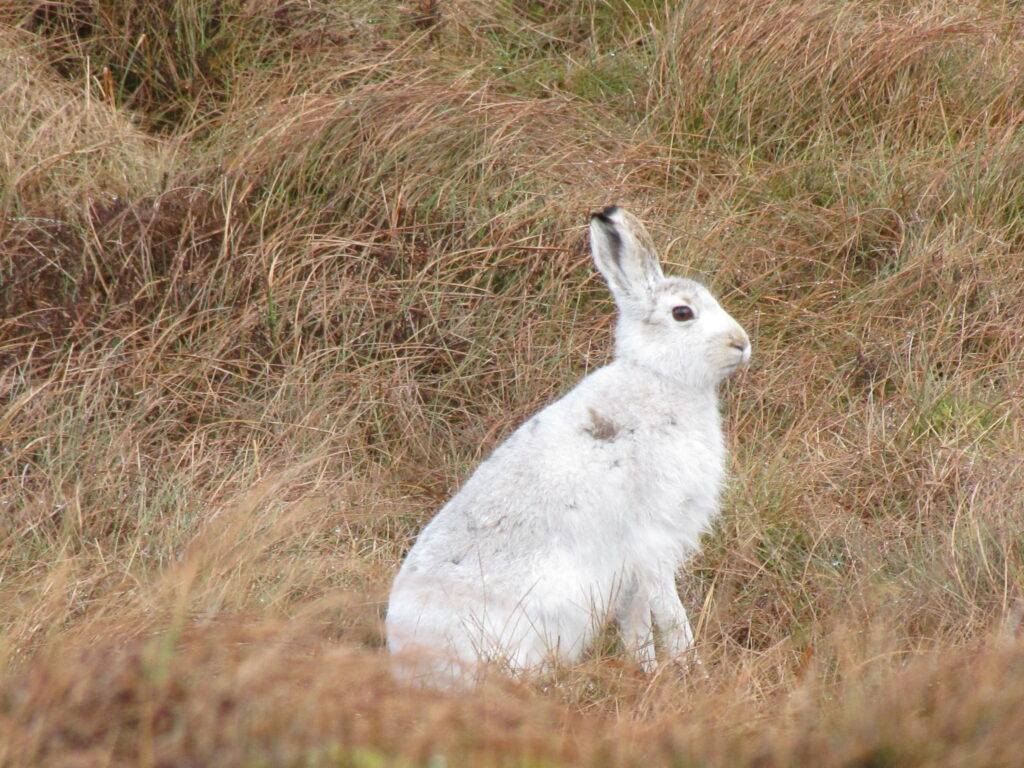


Irish hare (Lepus timidus hibernicus)
Distribution: Widespread across Ireland
What to look for: They are very visually similar to the mountain hare, except they do not develop a white coat during winter months and are noticeably smaller. During the summer, their coat is reddish-brown which dulls to grey-brown in winter, although their tail remains pure white.
Did you know? The Irish hare is a subspecies of the mountain hare and is the only lagomorph species native to Ireland. Fossil carbon dating suggests that these hares have been present in Ireland for at least 30,000 years.

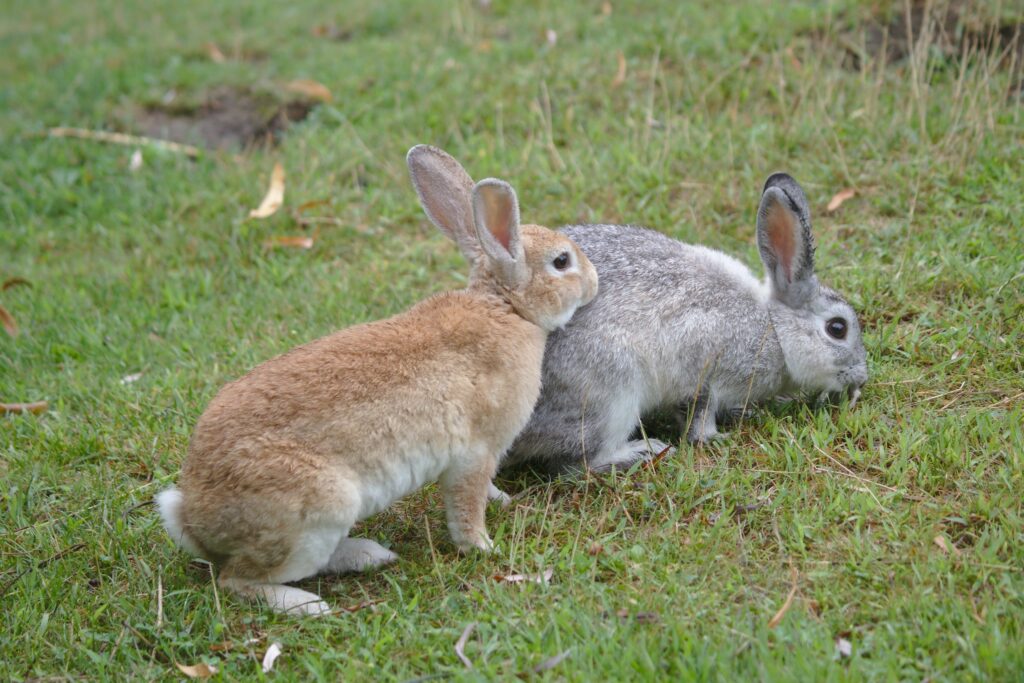
Domestic rabbit (feral) (Oryctolagus cuniculus domesticus)
Distribution: Unknown
What to look for: Domestic rabbits can have a huge variety of appearances, with at least 305 breeds of domestic rabbits around the world, although different numbers are accepted by different organisations. They can vary in size, colouration, body shape, coat type and ear length.
Did you know? Many pet rabbits are abandoned each year, particularly in the period after Easter.

Suggested reading:
 Britain’s Mammals: A Field Guide to the Mammals of Great Britain and Ireland
Britain’s Mammals: A Field Guide to the Mammals of Great Britain and Ireland
£17.99
 Guide to the Land Mammals of Britain
Guide to the Land Mammals of Britain
£3.75
 How to Find and Identify Mammals [Revised Edition]
How to Find and Identify Mammals [Revised Edition]
£11.99
All prices correct at the time of this article’s publication.







