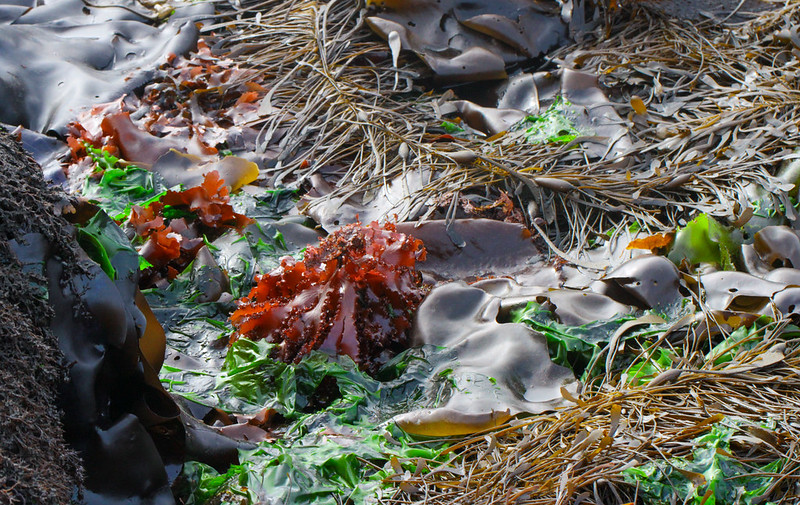

Seaweeds, or marine macroalgae, are plant-like organisms that live in coastal areas, usually attached to rocks or other substrates. They are divided into three taxonomic groups: brown, red and green. Broadly speaking, species fall into the group that most closely matches their colour. However, the groups also differ in more complex structural and biochemical features, such as their photosynthetic pigments and cell structure. While green and red seaweeds are classified in the Kingdom Plantae, which also includes all of the world’s land plants, brown seaweeds belong to the Kingdom Chromista and are more related to algae, diatoms and protozoans.
British and Irish seas are home to more than 600 species of seaweed; this is more than 6% of the known species globally. They are incredibly important ecologically and provide both food and shelter for numerous other creatures. In fact, one of the great pleasures of studying seaweeds is the many other species that you find along the way.
If you find yourself enjoying your seaweed studies, why not contribute to the Natural History Museum’s Big Seaweed Search. It only takes around an hour and will provide valuable data that can be used to research the effects of environmental change on our seashore communities.
When and where to find seaweed
Seaweed is present all year round. At low tide, more of the shore will be exposed which means that you are likely to find a greater range of species. This is also the only time that you are likely to spot a glimpse of those seaweeds that thrive in the lower intertidal zone. Sheltered shores tend to provide a better location for many species, as most cannot survive the battering of the waves in more exposed locations. However, there are a few species that are specially adapted to live on exposed shores so it’s always worth a look there. Similarly, as most species require a firm substrate to anchor to, rocky shores will be home to more seaweeds than sandy or muddy ones.
Ten common species to look for
Brown seaweeds:
Bladder wrack (Fucus vesiculosus)
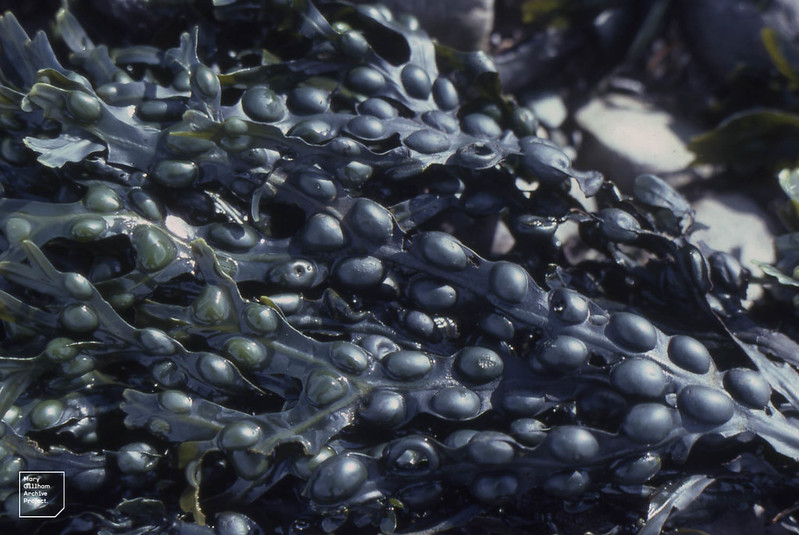

ID notes: An olive-brown seaweed that has branching fronds with smooth edges. Paired air-filled bladders run along the length of the fronds on either side of the central rib. 15-100cm in length. The number of bladders present is related to the exposure of the shore; in very exposed places this species may grow without any bladders and will also be much reduced in length.
Distribution: Found on rocky shores between the high and low water line.
Knotted wrack (Ascophylum nodosum)
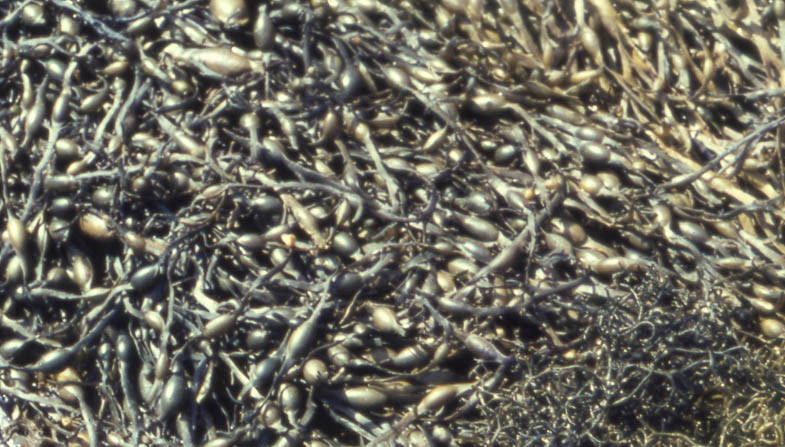

Also known as: Egg wrack
ID notes: This yellow-brown seaweed has long fronds reaching up to two metres in length. Single large air bladders appear at regular intervals along its length.
Distribution: Found on the mid-shore on sheltered rocky coasts. Knotted wrack is very long-lived (up to 15 years) in comparison to other algae; this allows it to become dominant on many sheltered coastlines. When the tide goes out it often forms huge piles.
Spiral wrack (Fucus spiralis)
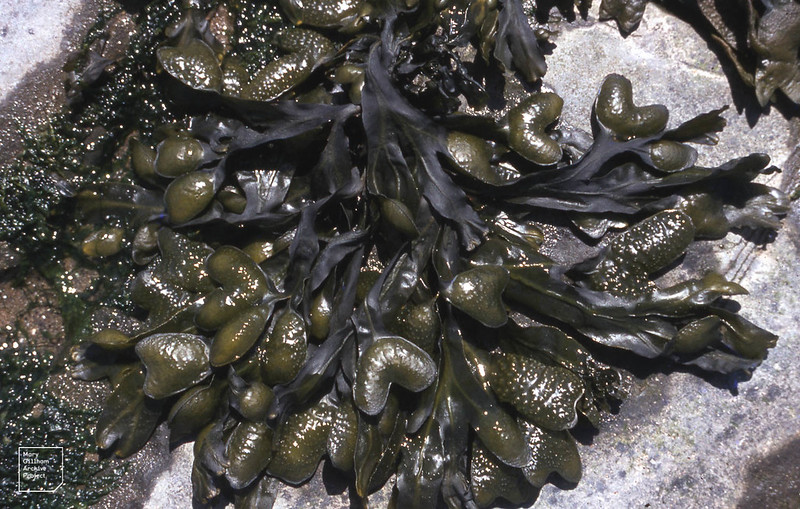

Also known as: Twisted wrack
ID notes: Spiral wrack is generally a pale olive-brown and grows up to 40cm. As the name would suggest, fronds are generally (although not always) twisted and have smooth edges and a distinct central rib. When mature, fronds have yellowish, paired swollen tips; these are the reproductive structures.
Distribution: Found high on the rocky shore, just below the high-water mark.
Serrated wrack (Fucus serratus)
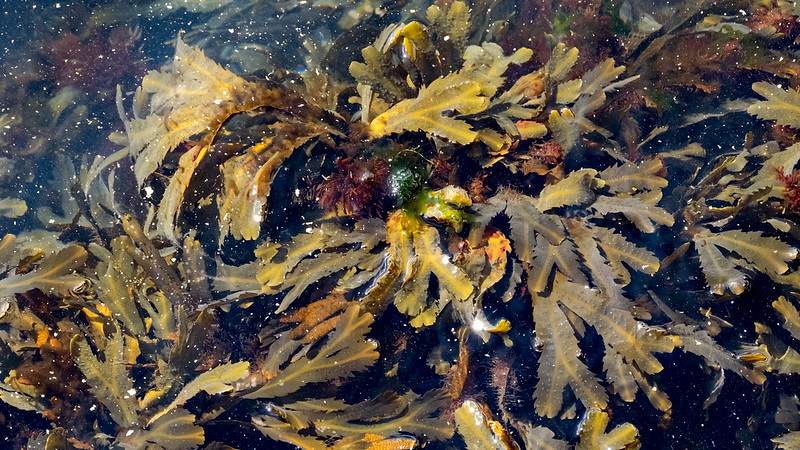

Also known as: Toothed wrack or saw wrack
ID notes: This brown seaweed forms branched fronds 50 to 80cm in length. Edges are serrated.
Distribution: Found on sheltered and semi-exposed rocky shores just above the low water mark. Fucus serratus is often the dominant algal species found at this point on the shoreline.
Oarweed (Laminaria digitata)
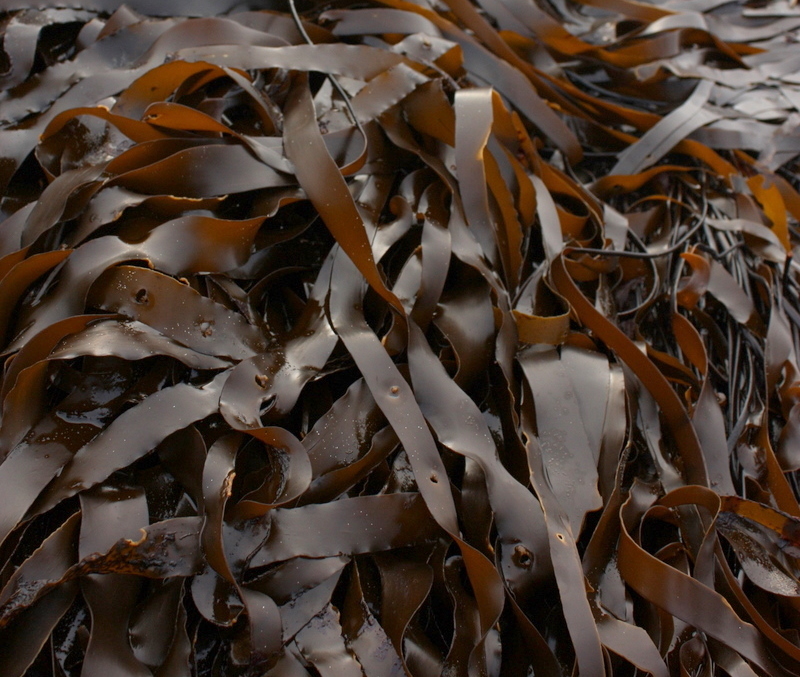

ID notes: Oarweed has dark brown-green fronds that are up to two metres in length and split into long finger-like blades. Attaches to the rock with a claw-like holdfast which allows it to survive in rough subtidal conditions.
Distribution: Grows in dense beds in the lower intertidal and shallow subtidal zones (at a depth of up to 20m). Often all that can be seen of this species are the tops of the fronds during low tide.
Sugar kelp (Saccharina latissimi)

Also known as: Sea belt
ID notes: Forms long undivided blades that are yellow-brown in colour and have ruffled sides. Grows up to five metres in length.
Distribution: Found on the lower shore and in deep rock pools. Mostly on sheltered shores and can be found up to a depth of 30m.
Green seaweeds:
Sea lettuce (Ulva lactua)
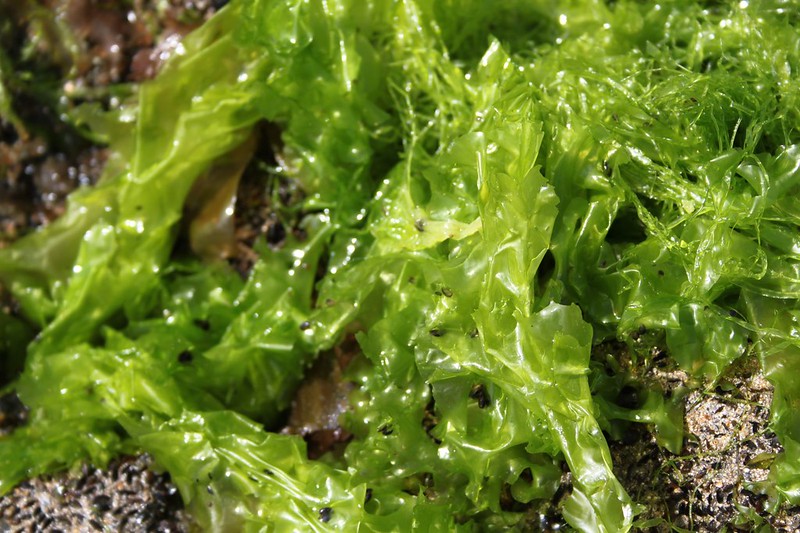

ID notes: Sheet-like light green seaweed which grows up to 25cm in length and 30cm in width. Very delicate and almost translucent; almost like floppy lettuce leaves.
Distribution: Found attached to rocks or floating in rock pools.
Gutweed (Ulva intestinalis)
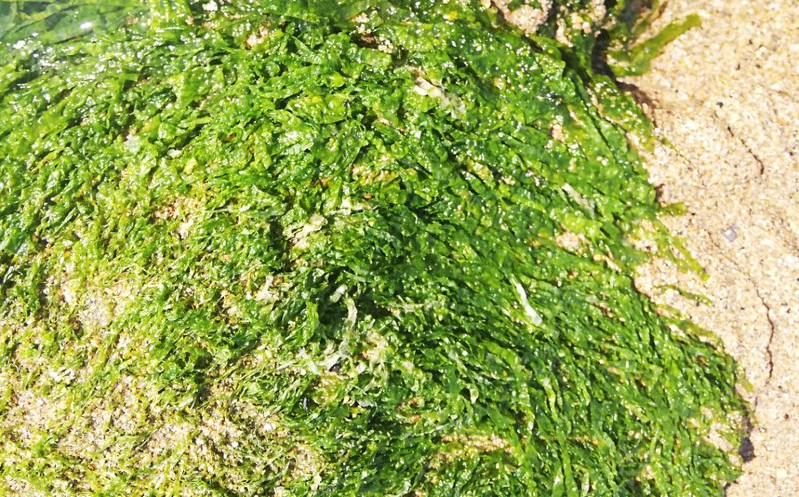

Also known as: Grass kelp
ID notes: As the Latin name would suggest, gutweed resembles the intestines of mammals and consists of inflated hollow fronds which have bubbles of air trapped along them. Bright green and grows up to 40cm in length.
Distribution: Occurs in a wide range of intertidal habitats including rockpools and on sand or mud. Can also be found growing on shells or other seaweeds.
Red seaweeds:
Carrageen (Chondrus crispus)
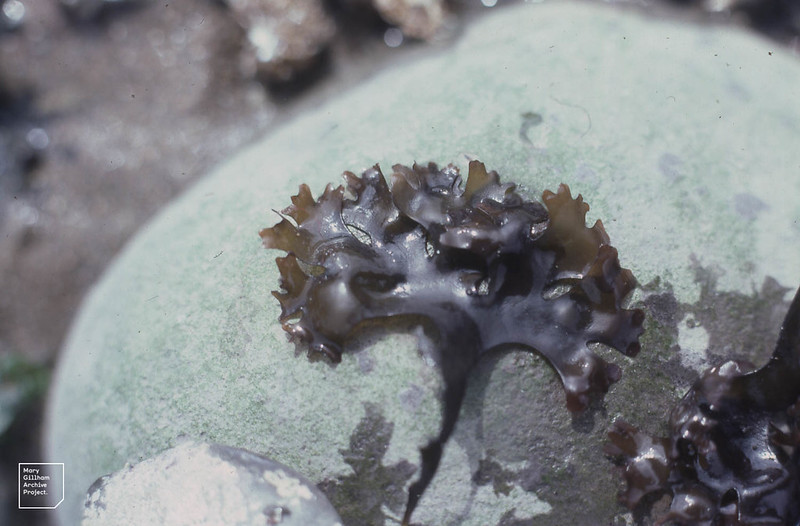

Also known as: Irish moss
ID notes: Dark reddish-purple branching seaweed which appears iridescent when submerged. Turns green with exposure to bright sunlight.
Distribution: Rocky shores and estuaries, on rocks and in pools in the lower intertidal and upper subtidal zones.
Purple laver (Porphyra umbilicalis)
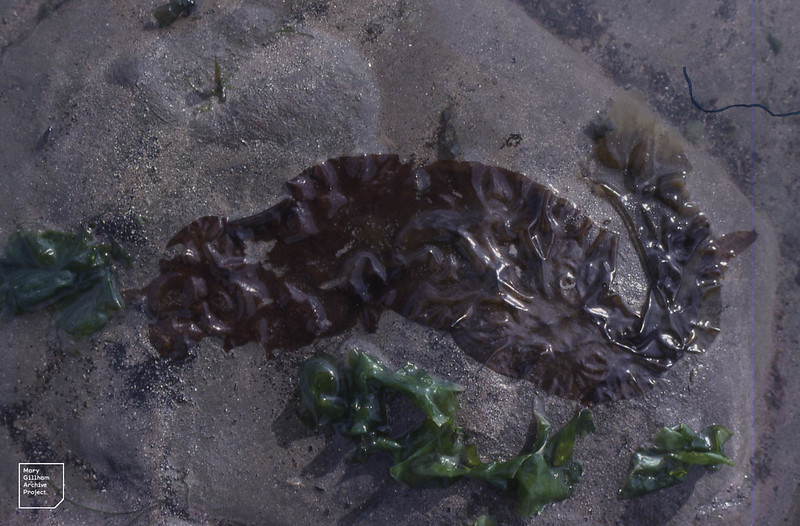

ID notes: Forms fronds of variable shape which are thin and membranous. Olive to purple-brown in colour and up to two metres in length.
Distribution: Found in the mid to upper shore, generally on mussel-covered rocks. Common on exposed coastlines.
Further reading
 A Key to Common Seaweeds
A Key to Common Seaweeds
#118696
This laminated guide from the FSC will help you to identify 36 of the most common seaweeds.
Seaweeds of Britain & Ireland
#235692
This photographic guide aims to demystify seaweed identification for the non-specialist. Over 235 species are described in detail, with colour photographs, information on habitat, distribution and confusion species.






